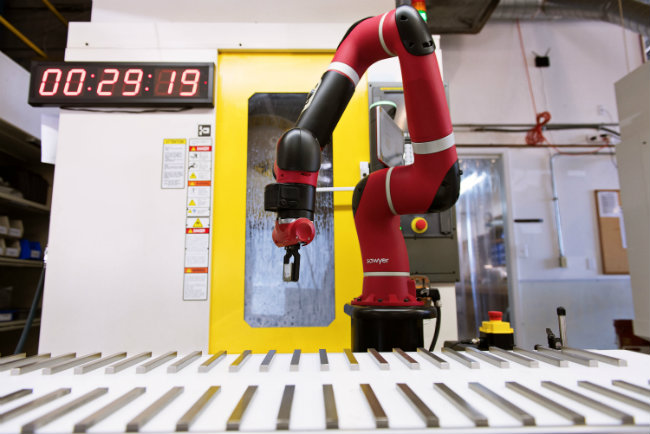
It is common knowledge that companies and educational institutions are doing what it takes to keep up with the ever-evolving field of automation. Robots and robotics impacts work and workplaces in new ways, every day.
Automation Changes Every Thing
Automation is changing how we live, how we work, and how we spend our free time. It improves quality of life and productivity. The supply and demand in most areas of commerce and business field are made easier because of various uses of automation. According to economists, the improvement of productivity that automation provides is positive for improving Gross Domestic Product (GDP), the value of goods and services produced in any given country.
Robots are a newish concept. However, since the beginning of making and providing goods and services, automation has existed. Consider the printing press, the steam engine, or a plow and compare them to a modern-time machine shop. Machine-tending robots utilize times when production would not occur. They also provide faster and more efficient work. However, while robots are on the rise, man and machine collaborate and work safely in the same space. ” Cobots” use sensors to allow humans and machines to work side-by-side in a machine shop or factory without incident.
Fear Not Robots
A custom machine shop is not the end of employing humans. No historical evidence exists that shows a significant technology impacting human employment levels. The fear that robots will take over stems from Western economies that include robots and automation. The trepidation and hesitation to utilize the latest technologies are unfounded. No one knows where the future of robots and automation will take the human race, but by all accounts, they are positive for all aspects of life.
Aspects of Automation
Companies like cnc automation continually examine the market of robots, machine shop technology, custom machined parts and all things’ automation. Every aspect requires constant consideration and the evolution of beliefs.
- The human workforce will remain competitive. Not all companies utilize automation and certainly not assign their labor to solely robots. Factors such as business size, geography, and payoff of the investment of automation technology. Companies that keep a mixed workforce are more productive than those that utilize only one or the other.
- The rise of robots sees safer work conditions. Workplace accidents come at a high cost, financially and personally. With the latest technology, the most dangerous of tasks are doable by robots. Strains from heavy lifting, exhaustion, and unsafe working conditions are no longer the norm.
- Automation drives job creation. Evidence shows that waves of technology have no effect on employment numbers. The opposite is actually true. As technology evolves, the number of required skills in a workplace grows.
- Three major industries predict a mostly mixed workplace. Healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics already are putting automation to work with their human labor force. The trend is expected to grow far larger and far faster in the future. Productivity, accuracy, and competition are the driving force in robots and humans working together.
- Workers report positive job satisfaction and a rewarding salary when automation is part of a company’s profile. Factors such as decentralized management structure, collaboration with multidisciplinary teams, the wide variety of tasks, and employee autonomy lead to positive workplace culture.
Robots & Manufacturing
Consumers now enjoy a wide-ranging variety of products. The increase in low volume, high mix manufacturing is obvious. Robots and automation is crucial when improving productivity in a non-challenging way. For example, Denver Manufacturing is a highly adaptable region where machine shops work to reduce manufacturing defects, lessen machine downtime, and decrease cost and loss of productivity.
One of the rising trends in automation and robotics is Cloud robotics. It is when data is collected and analyzed for productive and predictive purpose. Robots are becoming easier to afford, more adaptive to constant updates, and straightforward when reprogramming. Historically, larger businesses were the beneficiaries of robots. However, at a lower cost and easier to operate, everyone is seeing the rise in robots, in a factor or even in a personal home.
Factors that make automation and robotics available to all:
- Expansion in Company Visions
- Falling Prices in Components and Custom Machined Parts
- Mobility and Gripping Technology
- Cobot Evolution
- Sensory Technology
Robots — The New Coworker
Workers see an increase in responsibility of workflow and processes in factories and warehouses because of effective integration of robots. Other workers experience robots as direct coworkers and teammates. For example, robots and workers come together to assemble products or parts and pack them for delivery.
A collaborative robot is one that senses the environment and knows to move or react in tandem with a human counterpart. They work with human labor to lift a heavy object from one place to another for processing, get and carry parts that the worker requires, and perform precision manufacturing in a factory setting driven by human workers.
Actions possible with a collaborative robot includes:
- Weld
- Glue
- Mark
- Label
- Solder
- Lift and Place
The International Standards Organization (ISO) identifies four kinds of human and robot collaboration:
- Safety-rated monitored stop. “This is similar to the approach used with traditional industrial robots,” said Vladimir Murashov, a senior scientist in the Office of the Director at NIOSH and a member of the NIOSH Center for Occupational Robotics Research. “The work stops when a worker would like to enter the workspace of the robot.”
- Hand guiding is when a robot moves with the help of an operator.
- Speed and separation monitoring are when a robot slows or stops when human coworkers approach or touches it.
- Power and force limiting. “This is the approach that has really taken off in the marketplace, so it defines what everyone considers a ‘collaborative’ robot,” said Carole Franklin, director of standards development at the Robotic Industries Association. “Typically, these robots are limited in the payload they can carry and in the amount of force they could exert if they were to strike a person by accident. Also, the power/force-limited robots tend to be designed with rounded edges and softer surfaces that reduce the risk of injury if contact were to occur.”
New technology is often met with skepticism and anxiety. However, no evidence exists that robots take away human employment. Instead, it creates new jobs and optimal productivity. Interested in seeing Sawyer, a collaborative robot in a machine shop? Contact Tag Team Manufacturing in Parker, Colorado.